Positive Behavioral Interventions & Supports (PBIS) is defined as, “a framework or approach comprised of intervention practices and organizational systems for establishing the social culture, learning and teaching environment, and individual behavior supports needed to achieve academic and social success for all students” (Sugai et al., 2010, p. 13).
PBIS, is a broad range of systemic and individualized strategies for achieving important social and learning outcomes in school communities while preventing problem behavior. The key attributes of PBIS include preventive activities, data-based decision-making, and a problem-solving orientation (Horner, 2000; Lewis & Sugai, 1999; Sugai et.al., 2000; Weigle, 1997)
Schools implementing PBIS:
- Use a continuum of evidence-based practices to support student needs
- Engage students, families, and community members to co-create culturally responsive practices
- Regularly check the effectiveness of their practices
- Rely on teams to guide implementation
- Use data to identify strengths, uncover needs, and monitor student progress
- Implement universal screening
- Develop content expertise through coaching and on-going professional development
PBIS emphasizes four foundational and interrelated elements: 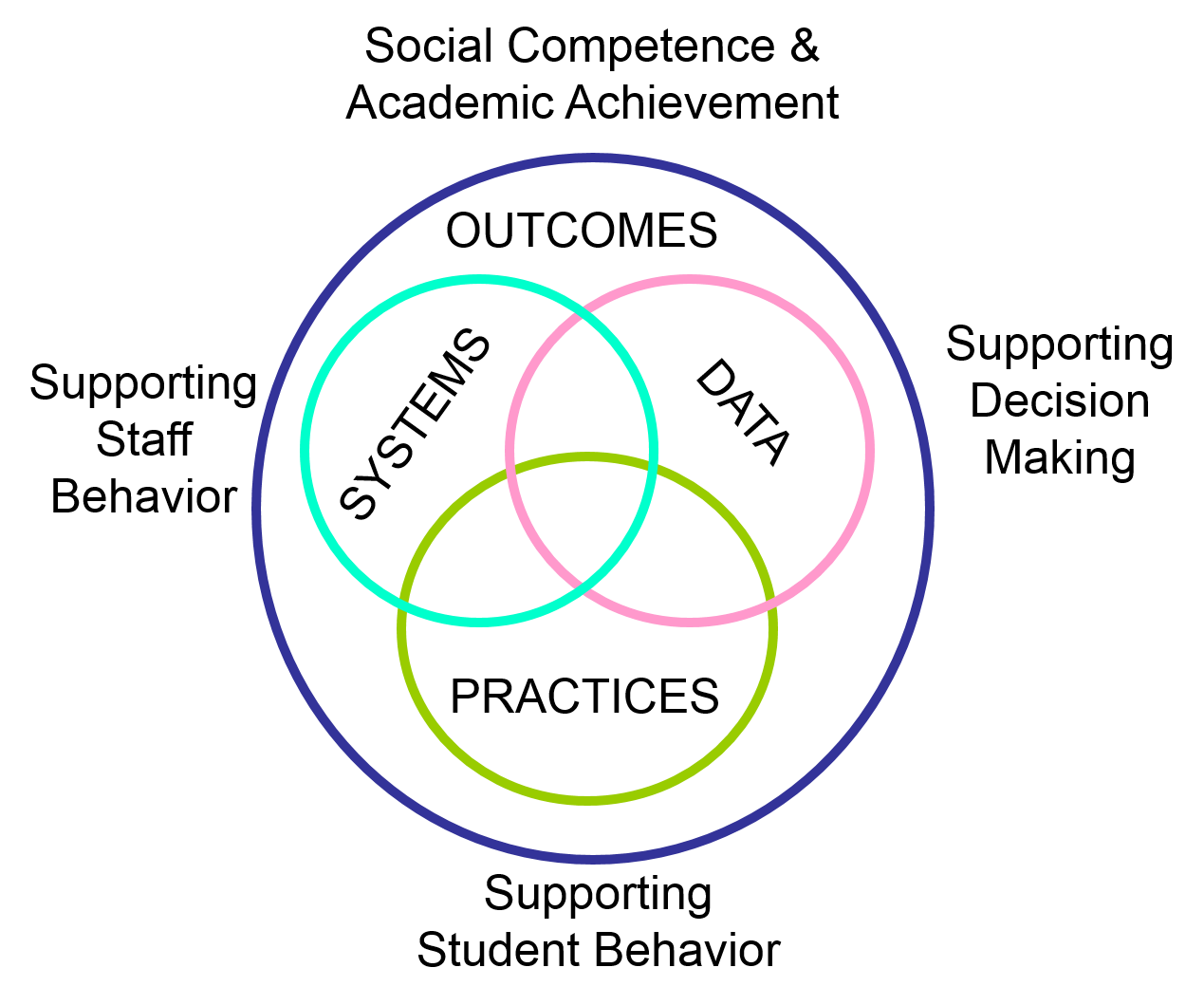
- locally meaningful and culturally relevant outcomes,
- empirically supported practices,
- systems that effectively support implementation,
- and data to monitor effective implementation, as well as to guide team decision-making.